
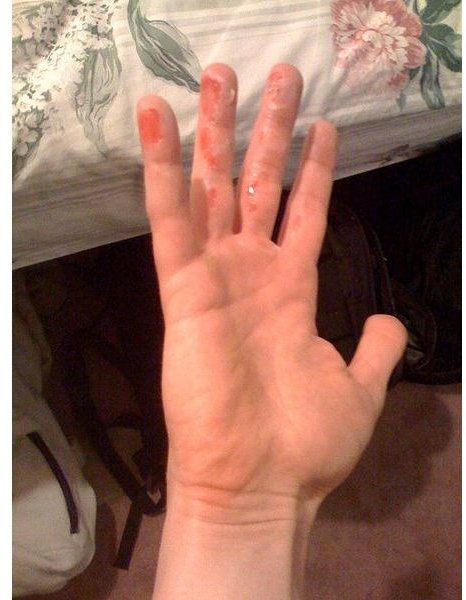
Generally, if the burn affects an area larger than the size of your palm, you should visit a doctor. Even second-degree burns to the hand should be examined by a doctor. If not treated properly, burns to the hand can cause permanent damage.
#Treating a rope burn skin#
The skin and tissue around the hand are sensitive. The location, severity, size, and side effects of the burn can all warrant a trip to the doctor in certain situations.īurns to the following areas should be examined by a doctor:īurns to the hand should be taken very seriously, especially with children. There are several scenarios where you will need to visit a doctor about your burn. When Should I Visit a Doctor For My Burn? If you or your child has an allergy, make sure to consult your doctor before using any medications or ointments. Ibuprofen, Advil, or other anti-inflammatory medications can help.

The surrounding skin may be numb as well. In some cases, the skin may appear charred or blackened.

Chemical burns and electricity can also cause third-degree burns.Ĭommon symptoms include intense blistering, reddening, and swelling of the skin. Third-degree burns can be caused by more prolonged exposure to hot objects such as boiling water or flames. These burns get deeper than first and second-degree burns and affect the underlying tissues. Third-degree burns are the worst level of burn. Second-degree burns cause more pain, including blisters, redness, and swelling around the burn. Even long exposure to the sun without protection can cause second-degree burns. These burns can be caused by electricity, sunburns, flames, or exposure to chemicals. Second-degree burns can reach the epidermis and the dermis (lower layer of skin). These are the most common burns caused by short exposure to heat from a hot pan or hot water, for example.Ĭommon symptoms of first-degree burns include reddening, sensitive, or dry skin but no blisters. First Degree Burnsįirst-degree burns are mild, superficial burns that only reach the epidermis (the outermost layer of skin). There are four major types of burn injuries. If you’ve been burned, the first thing you need to determine is just how bad the burn is. However, serious burns will require medical attention. Most burns are mild and can be treated with home remedies, such as Neosporin or aloe vera.
#Treating a rope burn how to#
Knowing how to treat your burn properly ensures that there’s no lasting damage to your skin or bones. Burns can happen anywhere and at any time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
